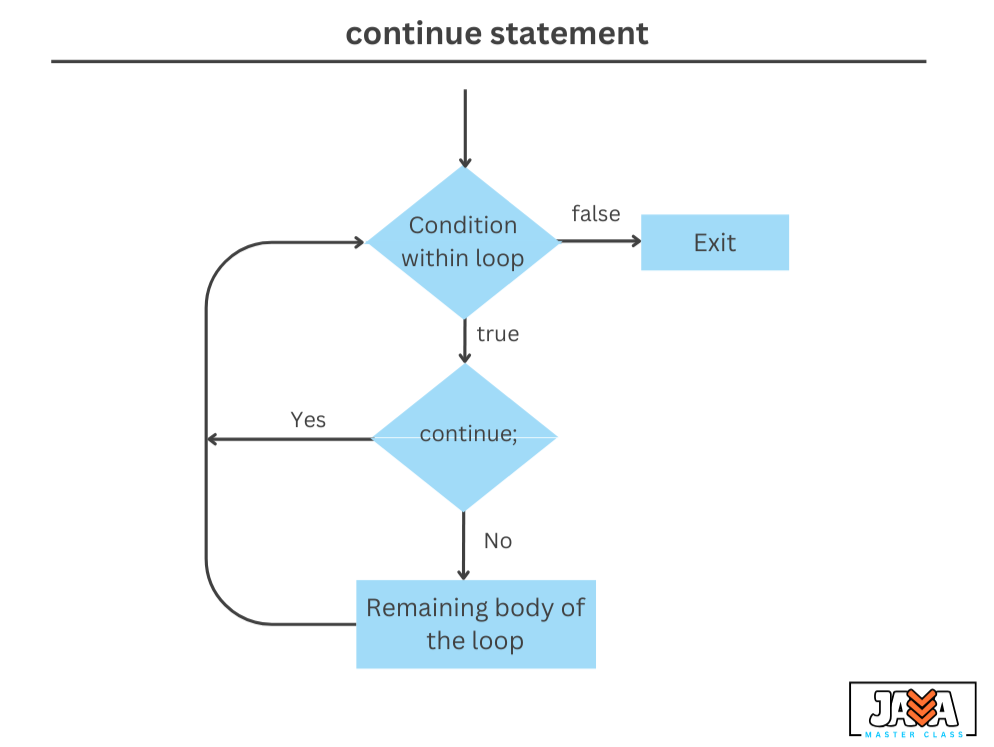
In Java, the continue statement is used within loops (such as for, while, or do-while) to skip the remaining code inside the loop for the current iteration and proceed to the next iteration. This control flow statement is very useful when you need to skip certain conditions and continue processing without completely exiting the loop.
Syntax
|
1 |
continue; |
It can be used in any loop structure where you want to skip the current iteration and move to the next one.
Examples
- For loops: When the
continuestatement is encountered, it immediately skips the rest of the code inside the loop and jumps to the next iteration of the loop. The loop’s condition is re-evaluated before proceeding.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
public class ContinueExample { public static void main(String[] args) { for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { if (i == 5) { continue; // Skip the rest of the loop when i equals 5 } System.out.println(i); } } } |
Output
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
1 2 3 4 6 7 8 9 10 |
The loop prints numbers from 1 to 10, but when i equals 5, the continue statement is executed. This causes the loop to skip the System.out.println(i) for that iteration, so 5 is never printed
- While and do-while loops: Similarly, in
whileanddo-whileloops, thecontinuestatement causes the loop to skip the rest of the current iteration and check the loop condition to decide whether to proceed with the next iteration.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
public class WhileContinueExample { public static void main(String[] args) { int i = 1; while (i <= 10) { if (i == 7) { i++; // Increment the counter before continuing continue; // Skip the current iteration when i equals 7 } System.out.println(i); i++; } } } |
Output
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
1 2 3 4 5 6 8 9 10 |
The loop prints numbers from 1 to 10, but when i equals 7, the continue statement is encountered, which skips the printing of 7. The value of i is incremented before the continue is executed to avoid an infinite loop.
