| Purpose |
Used to provide common functionality to related classes. |
Defines a contract for unrelated classes to follow. |
| Methods |
Can have both abstract methods (without implementation) and concrete methods (with implementation). |
Can have only abstract methods (prior to Java 8) and default methods (since Java 8). |
| Fields |
Can have fields (member variables). |
Cannot have fields, but can have constants. |
| Constructors |
Can have constructors. |
Cannot have constructors. |
| Inheritance |
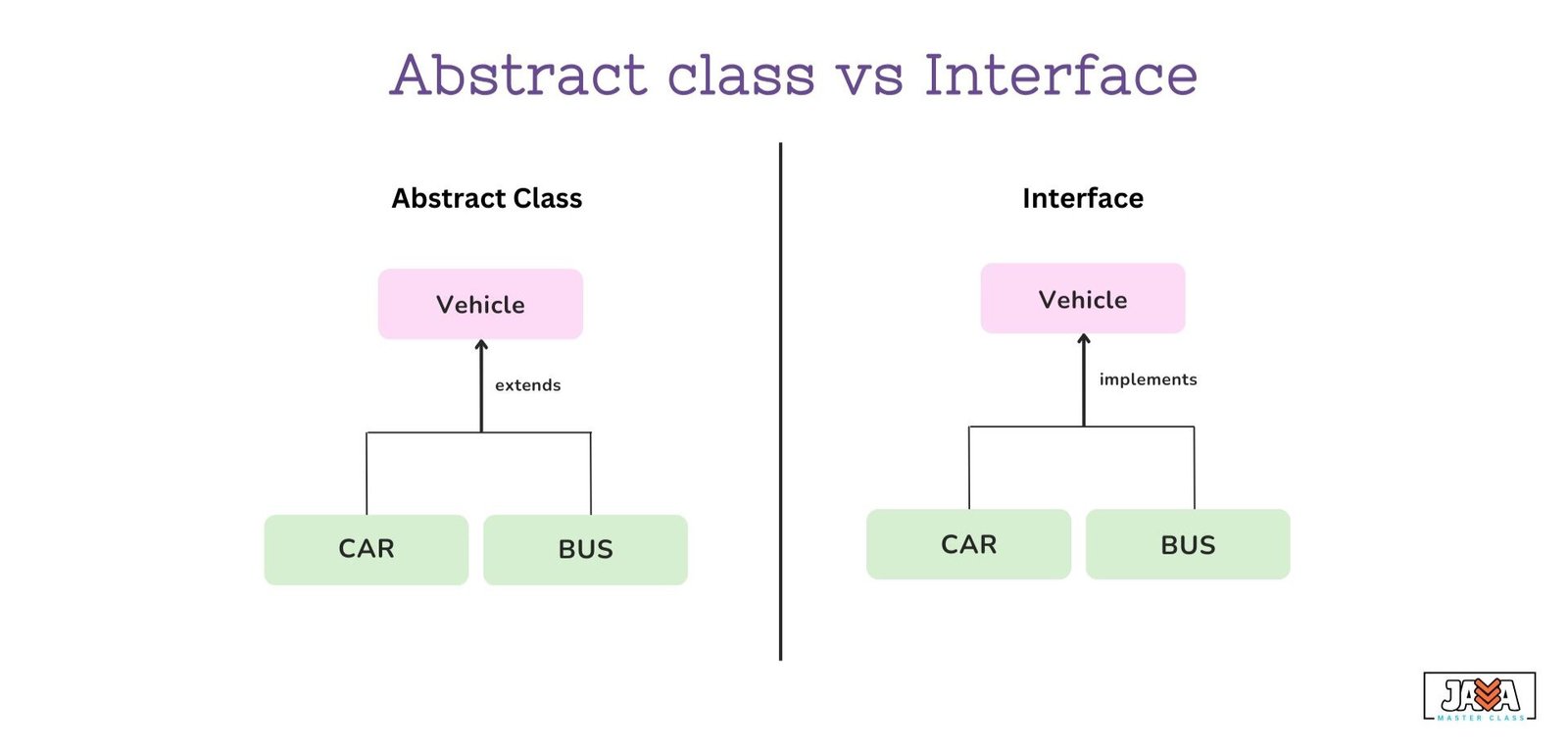
A class can extend only one abstract class. |
A class can implement multiple interfaces. |
| Access Modifiers |
Can use different access modifiers (private, protected, etc.). |
Methods are by default public (unless default methods). |
| Use Case |
Use when classes share some common behavior and need a base class. |
Use when you want to define a contract that multiple classes from different hierarchies can implement. |
| Example |
abstract class Vehicle { … } |
interface Drivable { void drive(); } |