Aspect-Oriented Programming (AOP) is a programming paradigm that allows separation of concerns, such as logging, transaction management, and security, from the core business logic. Spring AOP provides a way to implement these concerns in a modular way, enhancing code maintainability and readability.
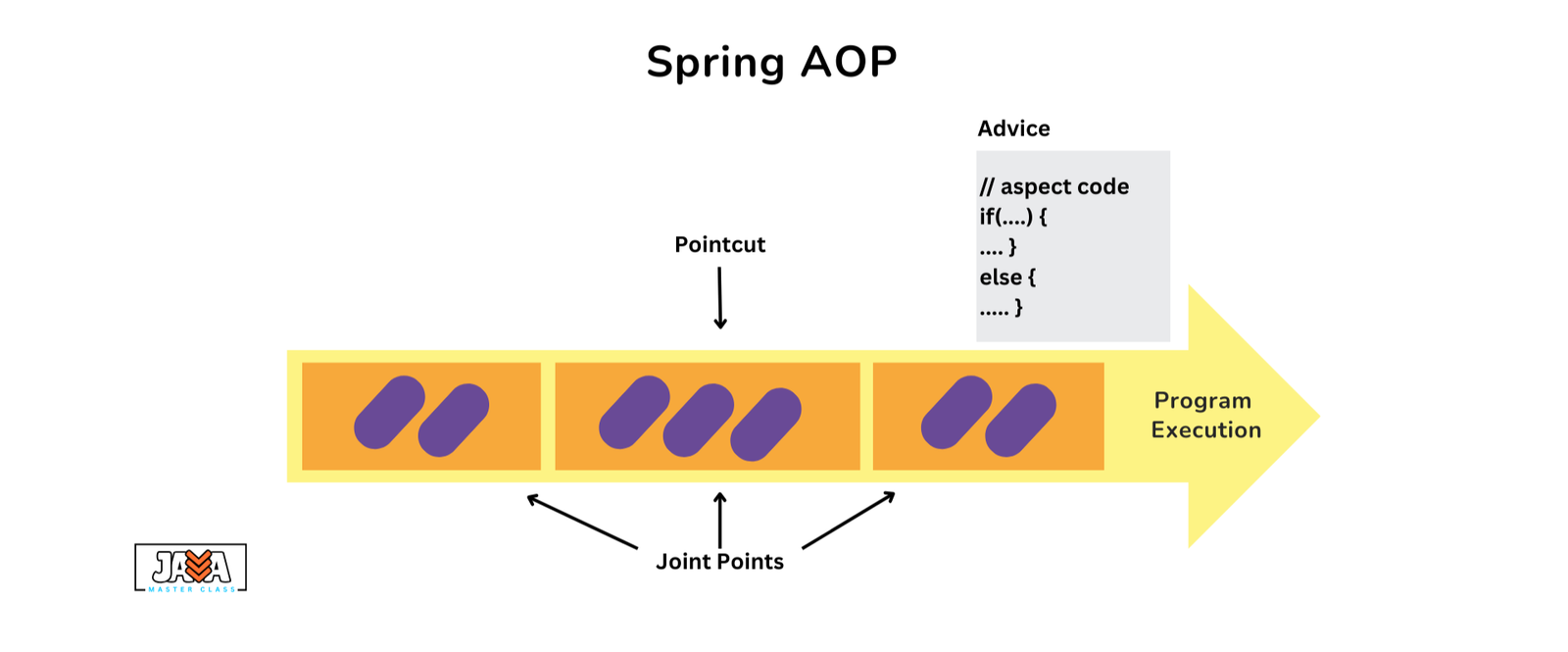
Concepts of AOP
- Aspect: A module that contains the cross-cutting logic, such as logging or security. An aspect is defined by using the
@Aspectannotation in Spring. - Join Point: A point in the execution of the program where you can apply an aspect. In Spring, join points typically refer to method executions.
- Advice: The action to be taken at a join point. Different types of advice include:
- Before: Code runs before the method is executed.
- After: Code runs after the method executes, regardless of its outcome.
- After Returning: Code runs after a method executes successfully.
- After Throwing: Code runs if the method throws an exception.
- Around: Code wraps the method execution. It allows modifying the method’s behavior before and after execution.
- Pointcut: A condition that matches join points where advice should be applied. Pointcuts can be specified using expressions, such as executing a method within a certain class or package.
- Weaving: The process of applying aspects to the code, which can be done at compile time, load time, or runtime. Spring AOP performs weaving at runtime.
Working of AOP in Spring
- Define an Aspect: Create a class annotated with
@Aspectand define methods with advice annotations like@Before,@After, etc. - Define a Pointcut: Use expressions to define where the advice should be applied. For example, applying an advice to methods in a specific package or class.
- Configure Spring AOP: Configure your Spring beans to enable AOP and specify the aspect to apply.
Example of Spring AOP
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
@Aspect @Component public class LoggingAspect { @Before("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))") public void logBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) { System.out.println("Before method: " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName()); } @After("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))") public void logAfter(JoinPoint joinPoint) { System.out.println("After method: " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName()); } } |
In the example above, the LoggingAspect class has two advices: logBefore runs before any method in the com.example.service package, and logAfter runs after any method in the same package.
Benefits of Spring AOP
- Separation of Concerns: It separates cross-cutting concerns (like logging, security) from business logic.
- Code Reusability: The same aspect can be applied to multiple methods or classes.
- Cleaner Code: Helps in keeping business logic focused and reduces clutter in the code.
Spring AOP is a powerful tool that, when used correctly, helps improve the organization and structure of your Java application.
