In Java applications, connecting to a database is often an expensive operation in terms of time and resources. Connection pooling helps by reusing a pool of pre-established database connections instead of creating new ones every time an operation is needed. This significantly improves performance and reduces overhead.
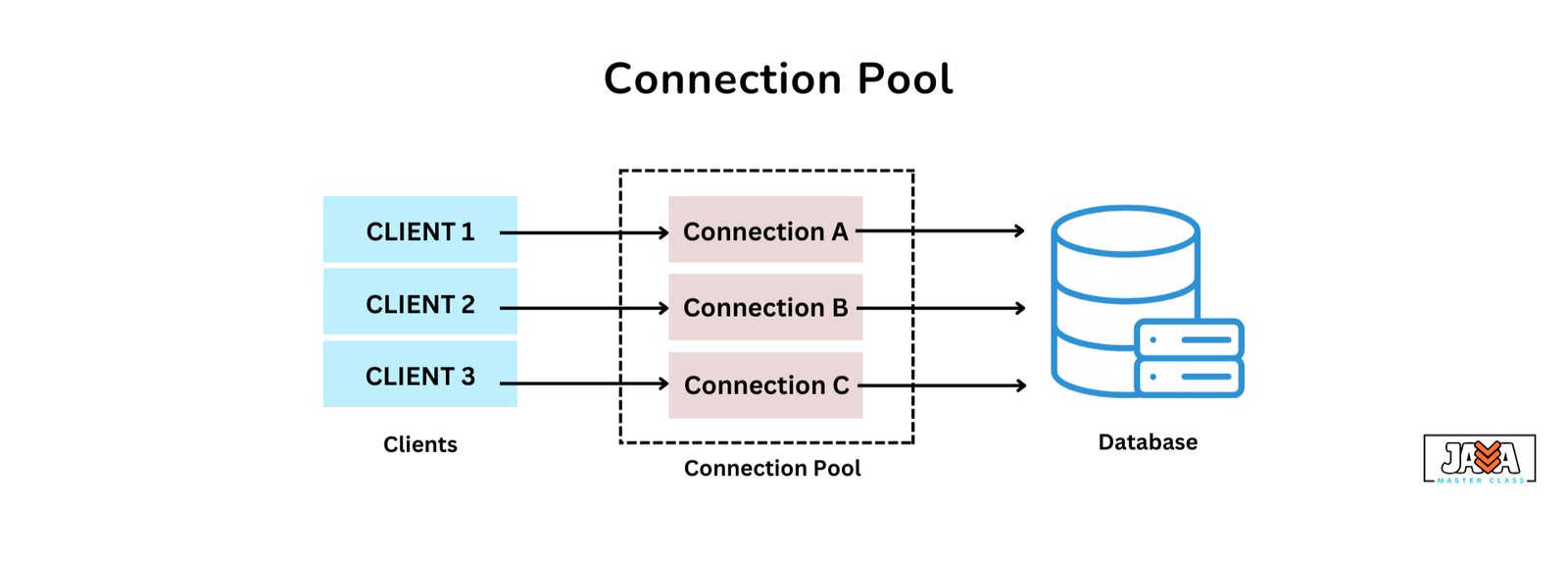
- Efficiency: Establishing a new connection to a database can be time-consuming. By reusing connections, the application can focus on performing queries rather than spending time on connection setup.
- Resource Management: Connection pools manage database connections efficiently, preventing excessive resource consumption.
- Scalability: With connection pooling, applications can handle a large number of concurrent database requests without overloading the system.
Connection Pooling Libraries
Apache DBCP (Database Connection Pooling)
- Apache DBCP is a popular and reliable connection pooling library.
- It provides a pool of database connections that can be reused, avoiding the overhead of frequently opening and closing connections.
- DBCP allows fine-grained control over connection properties, like validation and idle connection eviction.
- It’s widely used due to its simplicity and integration with Java EE servers.
Features of Apache DBCP
- Connection validation to check if a connection is valid before using it.
- Connection eviction strategy to close idle or stale connections.
- Integration with other Apache libraries for robust database management.
HikariCP
- HikariCP is a high-performance JDBC connection pool designed to be simple, efficient, and lightweight.
- It is known for its low-latency performance and is often favored for high-performance applications.
- It has a simple API, making it easy to configure and integrate into Java projects.
Features of HikariCP
- Fast Performance: HikariCP is optimized for high throughput and low-latency, making it the go-to choice for performance-critical applications.
- Minimal Overhead: It has a very small memory footprint, reducing the overhead compared to other connection pools.
- Built-in Metrics: Provides out-of-the-box metrics to monitor pool health and performance.
Implementation
Setting up a basic connection pool with Apache DBCP
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
// Create a BasicDataSource instance BasicDataSource dataSource = new BasicDataSource(); dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb"); dataSource.setUsername("username"); dataSource.setPassword("password"); // Configure pool properties dataSource.setMaxTotal(10); // Maximum number of connections dataSource.setMaxIdle(5); // Maximum idle connections // Get a connection from the pool Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection(); |
For HikariCP, the setup is equally simple
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
// Create a HikariDataSource instance HikariDataSource dataSource = new HikariDataSource(); dataSource.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb"); dataSource.setUsername("username"); dataSource.setPassword("password"); // Configure pool properties dataSource.setMaximumPoolSize(10); // Maximum pool size // Get a connection from the pool Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection(); |
